- Stem cells are the body’s raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated.
- Under certain conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells.
- These daughter cells either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or become specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells.
- No other cell in the body has the natural ability to generate new cell types.
Types of cells
Stem cells are of the following different types:
- Embryonic Stem Cells
- Adult Stem Cells
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- Mesenchymal stem cells
Embryonic Stem Cells
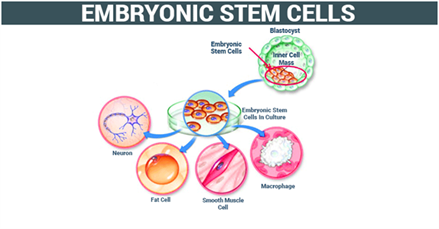
The fertilized egg begins to divide immediately. All the cells in the young embryo are totipotent cells. These cells form a hollow structure within a few days. Cells in one region group together to form the inner cell mass. This contains pluripotent cells that make up the developing foetus.
The embryonic stem cells can be further classified as:
- Totipotent Stem Cells: These can differentiate into all possible types of stem cells.
- Pluripotent Stem Cells: These are the cells from early embryo and can differentiate into any cell type.
- Multipotent Stem Cells: These differentiate into a closely related cell type. For eg., the hematopoietic stem cells differentiate into red blood cells and white blood cells.
- Oligopotent Stem Cells: Adult lymphoid or myeloid cells are oligopotent. They can differentiate into a few different types of cells.
- Unipotent Stem Cells: They can produce cells only of their own type. Since they have the ability to renew themselves, they are known as unipotent stem cells. For eg., Muscle stem cells.
Adult Stem Cells
These stem cells are obtained from developed organs and tissues. They can repair and replace the damaged tissues in the region where they are located. For eg., hematopoietic stem cells are found in the bone marrow. These stem cells are used in bone marrow transplants to treat specific types of cancers.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
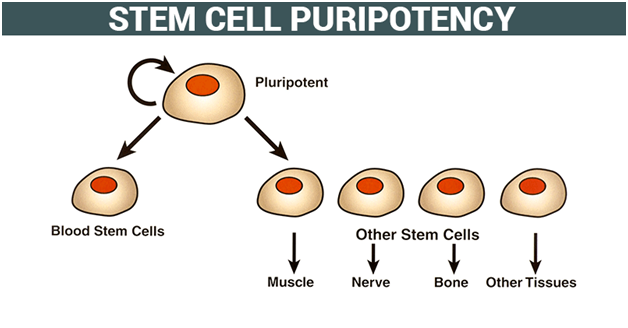
These cells have been tested and arranged by converting tissue-specific cells into embryonic cells in the lab. These cells are accepted as an important tool to learn about normal development, onset and progression of the disease and also helpful in testing various drugs. These stem cells share the same characteristics as embryonic cells do. They also have the potential to give rise to all the different types of cells in the human body.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
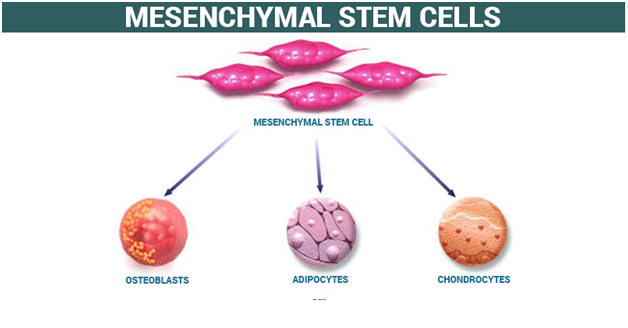
These cells are mainly formed from the connective tissues surrounding other tissues and organs known as stroma. These mesenchymal stem cells are accurately called stromal cells. The first mesenchymal stem cells were found in the bone marrow that are capable of developing bones, fat cells, and cartilage.
There are different mesenchymal stem cells that are used to treat various diseases as they have been developed from different tissues of the human body. The characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells depend on the organ from where they originate.
What is stem cell therapy?
- Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives.
- Stem cells can then be implanted into a person. For example Mumbai baby boy was injected with 40 million stem cells and gradually the lungs began to repair. In this case, doctors used mesenchymal stem-cell therapy (these are adult stem cells and are different from Embryonic stem cells) on an experimental basis
Why it is an issue?
- In March 2019, the Union Health Ministry had notified the ‘New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules, 2019’ which state that stem-cell derived products are to be used as “new drugs”. “This means that any doctor who uses stem-cell therapy needs to take permission from the government.
Advantages of Stem cell Therapy:
- Immense Medical Benefits: It offers a lot of medical benefits in the therapeutic cloning and regenerative medicine
- Treatment of Conditions and Disorders: It shows great potential in the treatment of a number of conditions like Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, cancer, diabetes and many others.
- A Better Knowledge of human growth: It helps the researchers know more about the growth of human cells and their development.
- The stem cell research can allow the scientists to test a number of potential medicines and drugs without carrying out any test on animals and humans. The drug can be tested on a population of cells directly.
- Cure development defects before they happen: The stem cell therapy also allows researchers to study the developmental stages that cannot be known directly through the human embryo and can be used in the treatment of a number of birth defects, infertility problems and also pregnancy loss. A higher understanding will allow the treatment of the abnormal development in the human body.
- Reduced risk of rejection: The stem cell therapy puts into use the cells of the patient’s own body and hence the risk of rejection can be reduced because the cells belong to the same human body.
Challenges in SCT
- Destruction of blastocysts: The use of the stem cells for research involves the destruction of the blastocysts that are formed from the laboratory fertilization of the human egg.
- Unknown side-effects: Like any other new technology, it is completely unknown what the long-term effects of such an interference with nature could be
- Limitations of adult cells: The disadvantage of adult stem cells is that the cells of a particular origin would generate cells only of that type, like brain cells would generate only brain cells and so on.
- Potential Rejection: If the cells used in the therapy are embryonic, then the cells will not be from the same human body and there are chances of rejection.
- Potential use in negative activities: It can be used to create bio-weapons or weapons of mass destruction
Applications of SCT
- Orthopedic injuries and musculoskeletal problems
- Wounds and incisions following surgeries
- Spinal cord injuries, brain trauma and spinal stenosis
- Cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke and congestive heart failure
- Hair loss
- Vision impairment
- Diabetes and other pancreatic dysfunctions
- Neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s
India and Stem Cell Therapy
- According to the Indian Council of Medical research, all stem cell therapy in India considered to be experimental except bone marrow transplants
- Stem cell therapy is legalized in India
- Umbilical cord and adult stem cell treatment are considered permissible
- Embryonic stem cell therapy and research is restricted



