CONTENTS
- Reorganising Andhra Pradesh
- Odisha’s Lingaraj temple ordinance
- Electoral bonds
- Weapons of Mass Destruction
- Sutlej Yamuna Link Canal
- Asian Development Outlook Report
Reorganising Andhra Pradesh
Context:
Recently, Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister inaugurated 13 new districts, pointing out that the main objective was to take the administration to the people’s doorsteps.
- The total number of districts has gone up to 26; and Andhra Pradesh has 25 Lok Sabha constituencies.
Relevance:
GS II- Polity and Governance
Dimensions of the Article:
- What are Districts?
- Procedure for creation of new districts in India
- Why has the AP government set up new districts?
- Who will the new districts serve?
- What happened to the ‘three capitals’ plan?
Click Here To Know More: Reorganising Andhra Pradesh
Odisha’s Lingaraj Temple Ordinance
Context:
The Central government has told the Odisha government that its ordinance to bring the 11th-century Lingaraj temple in Bhubaneswar and its associated temples under a special law is outside the legislative competence of the state legislature. It also said the ordinance is in conflict with the rules laid down under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 (AMASR Act).
Relevance:
GS I- Art and Architecture, GS II- Governance
Dimensions of the Article:
- Lingaraj Temple Ordinance, 2020
- Why has the Centre opposed the ordinance?
- Lingaraja Temple
Click Here To Know More: Odisha’s Lingaraj Temple Ordinance
Electoral bonds
Context:
Chief Justice of India N V Ramana has assured petitioners that the Supreme Court will take up for hearing a pending plea challenging the Electoral Bond Scheme, 2018. Two NGOs — Common Cause and Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) — have challenged the scheme, alleging that it is “distorting democracy”.
Relevance:
GS-II: Polity and Governance (Governance and Government Policies)
Dimensions of the Article:
- What are Electoral Bonds?
- Why have they attracted criticism?
- Government’s response defending the Electoral Bonds scheme
Click Here To Know More: Electoral bonds
Weapons of Mass Destruction
Context:
The Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Amendment Bill, 2022 has been unanimously passed in Lok Sabha.
Relevance:
GS III- Security Challenges, GS II- Government Policies and Interventions
Dimensions of the Article:
- Need of the Amendment
- Weapons of Mass Destruction
- Control over use of WMDs
Click Here To Know More: Weapons of Mass Destruction
Sutlej Yamuna Link Canal
Context:
The Haryana Vidhan Sabha has passed a resolution seeking completion of the Sutlej Yamuna Link Canal (SYL) Canal, bringing back into focus the contentious issue of sharing of river waters between Haryana and Punjab.

Relevance:
GS-I: Geography (Drainage System in India, Projects to improve Irrigation), GS-II: Polity and Governance (Inter-State Relations)
Dimensions of the Article:
- Sutlej Yamuna Link Canal
- Sharing of river waters
- Punjab’s argument
- Sutlej / Satluj River
- Yamuna River
Sutlej Yamuna Link Canal
- On April 8, 1982, then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi launched the construction of the SYL Canal with a groundbreaking ceremony in Kapoori village in Patiala district.
- A stretch of 214 km was to be constructed, out of which 122 km was to cross Punjab and 92 km in Haryana. But the Akalis launched an agitation in the form of Kapoori Morcha against the construction of the canal.
- Then in July 1985, Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi and then Akali Dal chief Sant Harchand Singh Longowal signed an accord agreeing for a new tribunal to assess the water.
- On August 20, 1985, Longowal was killed by militants, less than a month for signing the accord.
- In other violence, labourers were shot dead in Majat village near Chunni and Bharatgarh near Ropar.
- The construction came to a halt. In the backdrop of these incidents, Punjab leaders has been cautioning the Centre not to rake up the issue again.
The tribunal
- The Eradi Tribunal headed by Supreme Court Judge V Balakrishna Eradi was set up to reassess availability and sharing of water.
- In 1987, the tribunal recommended an increase in the shares of Punjab and Haryana to 5 MAF and 3.83 MAF, respectively.
Sharing of river waters
- The canal, once completed, will enable sharing of the waters of the rivers Ravi and Beas between the two states.
- The issue dates back to 1966 at the time of reorganisation of Punjab and formation of Haryana was formed.
- Punjab was opposed to sharing the waters of the two rivers with Haryana, citing riparian principles.
The shares
- A decade before the formation of Haryana, the water flowing down Ravi and Beas was assessed at 15.85 million acre feet (MAF) per year.
- The Union government had organised a meeting in 1955 between the three stake-holders — Rajasthan, undivided Punjab and Jammu and Kashmir — and allotted 8 MAF per year to Rajasthan, 7.20 MAF to undivided Punjab and 0.65 MAF to J&K.
- A decade after reorganisation, the Centre issued a notification allocating 3.5 MAF to Haryana out of the 7.2 MAF allotted to Punjab before reorganisation.
- In a reassessment in 1981, the water flowing down Beas and Ravi was estimated at 17.17 MAF, of which 4.22 MAF was allocated to Punjab, 3.5 MAF to Haryana, and 8.6 MAF to Rajasthan.
Punjab’s argument
- As per a state government study, many areas in Punjab may go dry after 2029.
- The state has already over-exploited its groundwater for irrigation purposes as it fills granaries of the Centre by growing wheat and paddy worth Rs 70,000 crore every year.
- As per reports, water in about 79% of the state’s area is over-exploited.
- Out of 138 blocks, 109 blocks are “over-exploited”, two blocks are “critical” five blocks are “semi-critical” and only 22 blocks are in “safe” category.
- In such a situation, the government says sharing water with any other state is impossible.
- Haryana has been staking claim to the Ravi-Beas waters through the SYL Canal on the plea that providing water for irrigation was a tough task for the state.
- In southern parts, where underground water had depleted up to 1700 feet, there was a problem of drinking water.
- Haryana has been citing its contribution to the central food pool and arguing that it is being denied its rightful share in the water as assessed by a tribunal.
Sutlej / Satluj River
- The Sutlej River is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan.
- It is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River.
- The waters of the Sutlej are allocated to India under the Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan, and are mostly diverted to irrigation canals in India.
- It has several major hydroelectric points, including the 1,325 MW Bhakra Dam, the 1,000 MW Karcham Wangtoo Hydroelectric Plant, and the 1,500 MW Nathpa Jhakri Dam.
- The drainage basin is mainly in India’s Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Jammu and Kashmir and Haryana states.
- The source of the Sutlej is west of the catchment area of Lake Rakshastal in Tibet, as springs in an ephemeral stream.
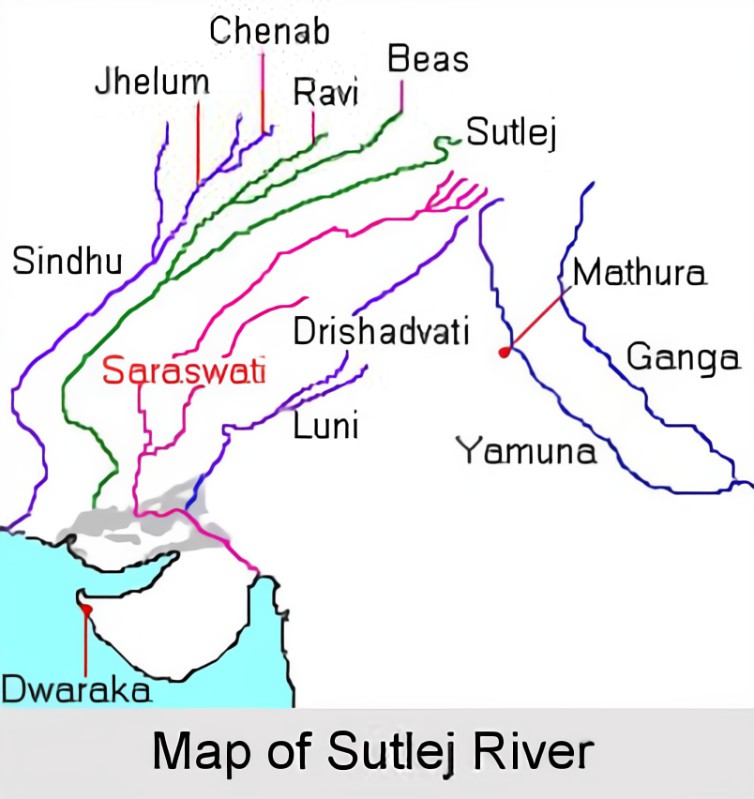
Yamuna River
- The river Yamuna, a significant tributary of the Ganges, flows from the Yamunotri glacier near the Bandarpoonch peaks in the Mussoorie range of the lower Himalayas, at an elevation of around 6387 metres above mean sea level in Uttarakhand’s Uttarkashi district.
- After flowing through Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, and Delhi, it meets the Ganges at the Sangam (where the Kumbh mela is held) in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh.
- 1376 kilometres in length
- Dams of note include the Lakhwar-Vyasi Dam in Uttarakhand and the Tajewala Barrage Dam in Haryana.
- Chambal, Sindh, Betwa, and Ken are important tributaries.

-Source: Indian Express
Asian Development Outlook Report
Context:
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) forecasts has provided some useful insights about India’s GDP growth.
Relevance:
GS III- Indian Economy
Dimensions of the Article:
- About Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Highlights of the ADB Outlook Report 2022
Click Here To Know More: Asian Development Outlook Report




