Why in news?
Helicopters of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) came close to the border during the face-off with the Indian Army near Pangong Tso lake in Eastern Ladakh.
As per existing agreements between India and China, operation of fighter aircraft and armed helicopters is restricted to a distance from the LAC.
According to the ‘Agreement on Maintenance of Peace and Tranquillity along the LAC in India-China Border Area’ of 1996, “combat aircraft (to include fighter, bomber, reconnaissance, military trainer, armed helicopter and other armed aircraft) shall not fly within 10 km of the LAC.”
Pangong Tso
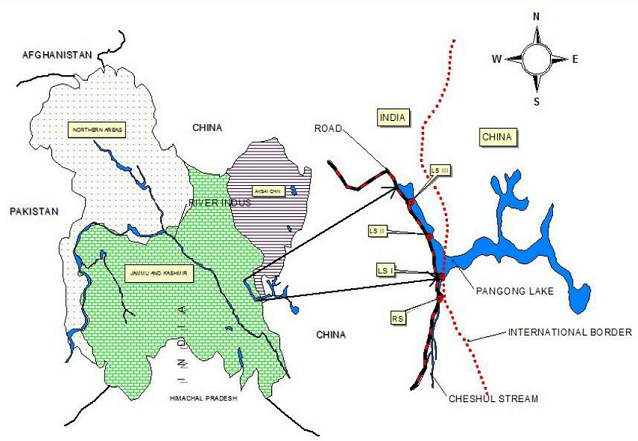
- Pangong Tso or Pangong Lake is an endorheic lake in the Himalayas situated at a height of about 4,350m.
- It is 134 km (83 mi) long and extends from India to the Tibetan Autonomous Region, China.
- Approximately 60% of the length of the lake lies within the Tibetan Autonomous Region.
- It is NOT a part of the Indus river basin area and geographically a separate landlocked river basin.
- The lake is in the process of being identified under the Ramsar Convention as a wetland of international importance.
Extra bits: Endorheic basin
An endorheic basin is a limited drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation.
Such a basin may also be referred to as a closed or terminal basin or as an internal drainage system or interior drainage basin.
-Source: The Hindu



